Data structure#
The most important file formats and data structures for cellpy are summarized here. It is also possible to look into the source-code at the repository jepegit/cellpy.
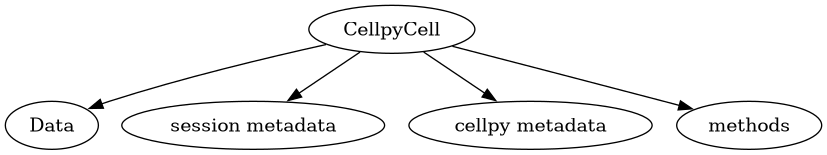
CellpyCell - main structure#
The CellpyCell is the main work-horse for cellpy, containing all the data, stored in the Data object, as well as all the functions for reading, selecting, and tweaking your data. It also contains the header definitions, both for the cellpy HDF5 format, and for the various cell-tester file-formats that can be read. The class can contain several tests and each test is stored in a list. The class also contains several attributes that can be assigned directly.
Methods#
The CellpyCell object contains lots of methods for manipulating, extracting
and summarising the data from the run(s).
The following two methods are typically automatically run upon loading your data using
cellpy.get(filename) and thereby creating your CellpyCell object:
make_step_table: creates a statistical summary of all the steps in the run(s) and categorizes the step type from that. It is also possible to give the step types directly (step_specifications).
make_summary: create a summary based on cycle number.
Other common methods worth mentioning are:
load: load a cellpy file.
load_raw: load raw data file(s) (merges automatically if several filenames are given as a list).
get_cap: get the capacity-voltage graph from one or more cycles in three different formats as well as optionally interpolated, normalized and/or scaled.
get_cycle_numbers: get the cycle numbers for your run.
get_ocv: get the rest steps after each charge and discharge step.
Take a look at API (Module index, cellpy.readers.cellreader.CellpyCell) for more info.
Data#
The data is stored as an instance of the Data class, CellpyCell.data
(a cellpy.cellreader.Data instance).
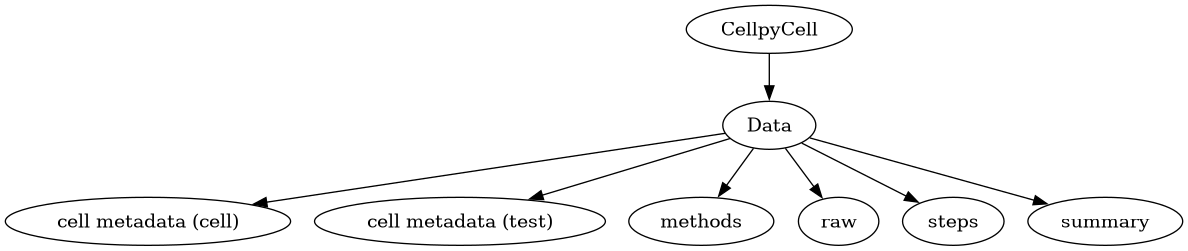
The Data object contains the data and the metadata for the cell characterisation experiment(s).
The actual measurement data, information, and summary are stored in three pandas.DataFrames:
raw: raw data from the run.
steps: stats from each step (and step type), created using theCellpyCell.make_step_tablemethod.
summary: summary data vs. cycle number (e.g. coulombic efficiency), created using theCellpyCell.make_summarymethod.
For details on column headings, see below.
Metadata#
The Data object contains the following metadata:
cell_no = None
mass = prms.Materials.default_mass # active material (in mg)
tot_mass = prms.Materials.default_mass # total material (in mg)
no_cycles = 0.0
charge_steps = None
discharge_steps = None
ir_steps = None
ocv_steps = None
nom_cap = prms.DataSet.nom_cap # mAh/g (for finding c-rates)
mass_given = False
material = prms.Materials.default_material
merged = False
file_errors = None # not in use at the moment
loaded_from = None # loaded from (can be list if merged)
channel_index = None
channel_number = None
creator = None
item_ID = None
schedule_file_name = None
start_datetime = None
test_ID = None
name = None
cycle_mode = prms.Reader.cycle_mode
active_electrode_area = None # [cm2]
active_electrode_thickness = None # [micron]
electrolyte_type = None #
electrolyte_volume = None # [micro-liter]
active_electrode_type = None
counter_electrode_type = None
reference_electrode_type = None
experiment_type = None
cell_type = None
separator_type = None
active_electrode_current_collector = None
reference_electrode_current_collector = None
comment = None
The Data object can also take custom metadata if provided as keyword arguments.
FileID#
The FileID object contains information about the raw file(s) and is used when comparing the cellpy-file
with the raw file(s) (for example to check if it has been updated compared to the cellpy-file).
Notice that FileID will contain a list of file identification parameters if the run is from several raw files.
Column headings#
Cellpy uses pandas.DataFrame objects internally. The column headers
of the dataframes are defined in corresponding dataclass objects that can be
accessed using both dot-notation and through normal dictionary look-up.
All the headers are set internally in cellpy and you can get them directly
by e.g.
from cellpy.parameters.internal_settings import headers_normal
cycle_column_header = headers_normal.cycle_index_txt
Column headings - raw data (or “normal” data)#
@dataclass
class HeadersNormal(BaseHeaders):
aci_phase_angle_txt: str = "aci_phase_angle"
ref_aci_phase_angle_txt: str = "ref_aci_phase_angle"
ac_impedance_txt: str = "ac_impedance"
ref_ac_impedance_txt: str = "ref_ac_impedance"
charge_capacity_txt: str = "charge_capacity"
charge_energy_txt: str = "charge_energy"
current_txt: str = "current"
cycle_index_txt: str = "cycle_index"
data_point_txt: str = "data_point"
datetime_txt: str = "date_time"
discharge_capacity_txt: str = "discharge_capacity"
discharge_energy_txt: str = "discharge_energy"
internal_resistance_txt: str = "internal_resistance"
power_txt: str = "power"
is_fc_data_txt: str = "is_fc_data"
step_index_txt: str = "step_index"
sub_step_index_txt: str = "sub_step_index"
step_time_txt: str = "step_time"
sub_step_time_txt: str = "sub_step_time"
test_id_txt: str = "test_id"
test_time_txt: str = "test_time"
voltage_txt: str = "voltage"
ref_voltage_txt: str = "reference_voltage"
dv_dt_txt: str = "dv_dt"
frequency_txt: str = "frequency"
amplitude_txt: str = "amplitude"
channel_id_txt: str = "channel_id"
data_flag_txt: str = "data_flag"
test_name_txt: str = "test_name"
Column headings - summary data#
@dataclass
class HeadersSummary(BaseHeaders):
"""In addition to the headers defined here, the summary might also contain
specific headers (ending in _gravimetric or _areal).
"""
postfixes = ["gravimetric", "areal"]
cycle_index: str = "cycle_index"
data_point: str = "data_point"
test_time: str = "test_time"
datetime: str = "date_time"
discharge_capacity_raw: str = "discharge_capacity"
charge_capacity_raw: str = "charge_capacity"
test_name: str = "test_name"
data_flag: str = "data_flag"
channel_id: str = "channel_id"
coulombic_efficiency: str = "coulombic_efficiency"
cumulated_coulombic_efficiency: str = "cumulated_coulombic_efficiency"
discharge_capacity: str = "discharge_capacity"
charge_capacity: str = "charge_capacity"
cumulated_charge_capacity: str = "cumulated_charge_capacity"
cumulated_discharge_capacity: str = "cumulated_discharge_capacity"
coulombic_difference: str = "coulombic_difference"
cumulated_coulombic_difference: str = "cumulated_coulombic_difference"
discharge_capacity_loss: str = "discharge_capacity_loss"
charge_capacity_loss: str = "charge_capacity_loss"
cumulated_discharge_capacity_loss: str = "cumulated_discharge_capacity_loss"
cumulated_charge_capacity_loss: str = "cumulated_charge_capacity_loss"
normalized_charge_capacity: str = "normalized_charge_capacity"
normalized_discharge_capacity: str = "normalized_discharge_capacity"
shifted_charge_capacity: str = "shifted_charge_capacity"
shifted_discharge_capacity: str = "shifted_discharge_capacity"
ir_discharge: str = "ir_discharge"
ir_charge: str = "ir_charge"
ocv_first_min: str = "ocv_first_min"
ocv_second_min: str = "ocv_second_min"
ocv_first_max: str = "ocv_first_max"
ocv_second_max: str = "ocv_second_max"
end_voltage_discharge: str = "end_voltage_discharge"
end_voltage_charge: str = "end_voltage_charge"
cumulated_ric_disconnect: str = "cumulated_ric_disconnect"
cumulated_ric_sei: str = "cumulated_ric_sei"
cumulated_ric: str = "cumulated_ric"
normalized_cycle_index: str = "normalized_cycle_index"
low_level: str = "low_level"
high_level: str = "high_level"
temperature_last: str = "temperature_last"
temperature_mean: str = "temperature_mean"
charge_c_rate: str = "charge_c_rate"
discharge_c_rate: str = "discharge_c_rate"
pre_aux: str = "aux_"
Column headings - step table#
@dataclass
class HeadersStepTable(BaseHeaders):
test: str = "test"
ustep: str = "ustep"
cycle: str = "cycle"
step: str = "step"
test_time: str = "test_time"
step_time: str = "step_time"
sub_step: str = "sub_step"
type: str = "type"
sub_type: str = "sub_type"
info: str = "info"
voltage: str = "voltage"
current: str = "current"
charge: str = "charge"
discharge: str = "discharge"
point: str = "point"
internal_resistance: str = "ir"
internal_resistance_change: str = "ir_pct_change"
rate_avr: str = "rate_avr"
Step types#
Identifiers for the different steps have pre-defined names given in the
class attribute list list_of_step_types and is written to the “step” column.
list_of_step_types = ['charge', 'discharge',
'cv_charge', 'cv_discharge',
'charge_cv', 'discharge_cv',
'ocvrlx_up', 'ocvrlx_down', 'ir',
'rest', 'not_known']
Column headings - journal pages#
@dataclass
class HeadersJournal(BaseHeaders):
filename: str = "filename"
mass: str = "mass"
total_mass: str = "total_mass"
loading: str = "loading"
area: str = "area"
nom_cap: str = "nom_cap"
experiment: str = "experiment"
fixed: str = "fixed"
label: str = "label"
cell_type: str = "cell_type"
instrument: str = "instrument"
raw_file_names: str = "raw_file_names"
cellpy_file_name: str = "cellpy_file_name"
group: str = "group"
sub_group: str = "sub_group"
comment: str = "comment"
argument: str = "argument"
CellpyCell.keys_journal_session = ["starred", "bad_cells", "bad_cycles", "notes"]
Tester-dependent attributes#
For each type of testers that are supported by cellpy,
a set of column headings and other different settings/attributes might also exist.
These definitions stored in the cellpy.parameters.internal_settings module and
are also injected into the CellpyCell class upon initiation.